Background and objectives
The recommended initial tests for suspected Cushing’s syndrome are late-night salivary cortisol (LNSC), 24-hour urinary free cortisol (UFC) and the 1 mg overnight dexamethasone suppression test (ONDST). These tests have higher sensitivity and specificity than serum cortisol. The aim of this study was to determine the relative frequency of these requested tests in primary care.
Methods
Initial test selection for investigation of Cushing’s syndrome was audited by reviewing pathology request forms for cortisol tests made to a major community-based laboratory in 2019. Those with hypertension or adrenal incidentaloma as the documented indication for testing were included.
Results
In 214 of 272 cases (78.7%; 95% confidence interval: 73.2%, 83.3%) initial testing was by measurement of serum cortisol alone.
Discussion
The relatively infrequent selection of the higher sensitivity tests (ONDST, UFC and LNSC) for investigation of suspected Cushing’s syndrome signifies a risk of delayed or missed diagnosis, with important implications for morbidity and mortality.
Clinicians are faced with an increasing number of patients requiring exclusion of Cushing’s syndrome, in the setting of a rising prevalence of hypertension and metabolic syndrome,1,2 as well as greater use of medical imaging that can detect adrenal incidentalomas (adrenal mass lesions serendipitously discovered by radiological examination in the absence of clinical features).3 Diagnosis of Cushing’s syndrome requires clinical suspicion and reliable biochemical testing. Owing to their high sensitivity and specificity, the recommended initial tests for suspected Cushing’s syndrome are late-night salivary cortisol (LNSC), 24-hour urinary free cortisol (UFC) and 1 mg overnight dexamethasone suppression test (ONDST; preferred for patients with adrenal incidentalomas).3,4 Loss of diurnal variation is a key biochemical feature of Cushing’s syndrome; evening and total daily secretion of cortisol are increased, but morning concentrations are often unaffected. Measurement of random or morning serum cortisol is not useful or recommended because of the considerable overlap between daytime levels in healthy patients and those with Cushing’s syndrome.5
Methods
We audited the initial selection of tests for Cushing’s syndrome in primary care by examining requests made to our major community-based laboratory in 2019. Pathology request forms for cortisol tests were reviewed to select those who had a documented clinical history consistent with investigation for Cushing’s syndrome; this included hypertension and adrenal incidentaloma. Analysis, including determination of Wilson score confidence intervals (CIs) and comparison of proportions by χ2-tests, was carried out in Microsoft Excel and RStudio. The present study was approved by the PathWest Quality Improvement Committee (approval no. 42561).
Results
In 214 of 272 cases (78.7%; 95% CI: 73.2%, 83.3%), initial testing was by measurement of serum cortisol alone. In cases of adrenal incidentaloma, ONDST (the preferred test in this clinical scenario) comprised 14 of 39 requests (35.9%; 95% CI: 21.7%, 52.8%; Figure 1). This was significantly higher (P = 0.006) than the proportion of hypertension cases investigated with a recommended test for this condition (ie ONDST, UFC or LNSC [37 of 234 requests, 15.8%; 95% CI: 11.5%, 21.3%]).
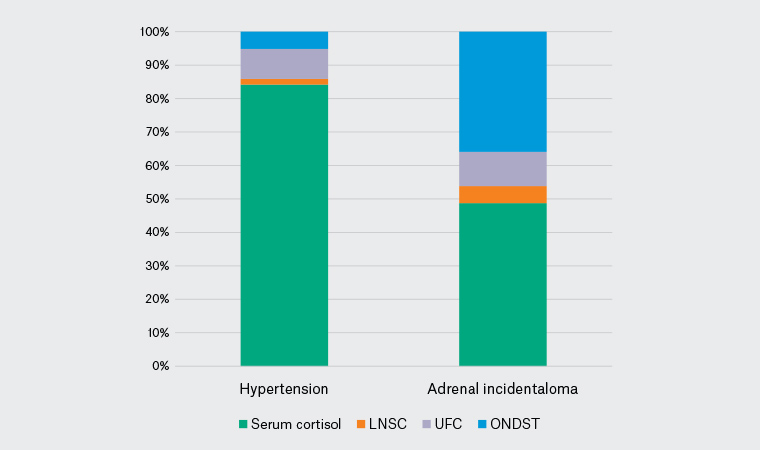
Figure 1. Cortisol test selection by clinical history
LNSC, late-night salivary cortisol; ONDST, overnight dexamethasone suppression test; UFC, urinary free cortisol
Discussion
The relatively low use of the higher sensitivity tests (ONDST, UFC and LNSC) signifies a risk of delayed or missed diagnosis of Cushing’s syndrome, with important implications for morbidity and mortality.
Limitations of this study include that cortisol tests were only examined for two clinical conditions. We did not explore potential differences in tests requested based on geographical area or level of clinical experience of requestors. We advise clinicians to avoid requesting measurement of serum cortisol when suspecting Cushing’s syndrome and to instead opt for a test with greater sensitivity and specificity, to help ensure patients are correctly identified and can be appropriately treated. Medical educators and pathology services have important roles in supporting pathology requesting in this area. The incorporation of decision-support prompting in clinical software should also be explored.