Tremor is defined by the International Parkinson and Movement Disorder Society as an involuntary, rhythmic, oscillatory movement of a body part.1 Tremor is a common, physically and psychosocially debilitating symptom frequently encountered in clinical practice.1,2 Tremor is often one clinical feature of a disease process and has a diverse range of aetiologies. This paper outlines an approach to the evaluation of tremor, the most common tremor syndromes and important clinical masquerades.
Describing tremor
Developing an approach to describe tremor is required to effectively evaluate and monitor response to treatment. To systematically assess tremor, describe each of the characteristics listed in Table 1, beginning with the activating condition and location. Other observed characteristics include axis, amplitude, constancy, frequency and regularity.1,3 Table 1 provides detailed explanations of these characteristics and the clinical relevance of each.
|
Table 1. Definitions of different characteristics used to describe tremor and the clinical relevance of each
|
|
Term
|
Explanation
|
Clinical relevance
|
|
Activating condition
|
- The activating condition specifies whether a tremor is a rest or action tremor
- An action tremor is further categorised into specific action: postural, kinetic, isometric or intention tremor
|
- PD is commonly associated with rest tremor, compared with the kinetic tremor noted in ET
- An asymmetric rest tremor is often present during walking in PD patients
|
|
Location
|
- Refers to the body part or parts where the tremor is manifested (ie upper limbs, lower limbs, head/neck and voice) and whether it is symmetrical
|
- An asymmetric upper limb rest tremor is common at the onset of PD16
- ET typically presents with a symmetric upper limb kinetic tremor4
- Head/neck tremor is more common in dystonic tremor or ET4,17,24
|
|
Axis
|
- Describes the plane or direction in which the tremor occurs around a joint
|
- PD tremor often has a characteristic distal axis (ie pill-rolling tremor)4
- ET is more likely to have a proximal axis (eg wrist flexion and extension axis of tremor)4
|
|
Amplitude
|
- The distance of movement, often described as fine, moderate or coarse25
|
- Amplitude relates to the severity of tremor in PD26
- In ET, typically the amplitude of kinetic tremor is greater than postural tremor7
|
|
Constancy
|
- Observe the proportion of time a rest tremor is present during an examination
|
- Patients in the earlier stages of PD may have an intermittent rest tremor14
- In ET, tremor is constantly present during kinetic movements4
|
|
Regularity
|
- A regular tremor has uniform oscillations, whereas an irregular tremor has variable oscillations
|
- Functional tremor is often irregular and distractable21
- Position- or task-specific tremor with irregular ‘flurries’ of tremor suggest dystonic tremor27
|
|
Frequency
|
- Refers to the rate of oscillation of the tremor and is often classified as low frequency (<4 Hz), medium frequency (4–7 Hz) or high frequency (>7 Hz)
|
- Frequency may be low (eg rubral tremor), medium (eg PD, ET) or high (eg enhanced physiological tremor or orthostatic tremor)27
|
|
ET, essential tremor; PD, Parkinson’s disease.
|
History
History taking is vital to consider the aetiology of a tremor presentation. Table 2 outlines the key aspects a clinician may evaluate in taking a focused tremor history. Particular reference is made to different features of common tremor syndromes.
Examination
Examining a patient’s tremor requires careful observation and a methodical approach. Techniques that can supplement general inspection, vital signs and a thorough neurological examination for associated features (eg extrapyramidal features) are presented in Table 3.
Tremor syndromes
After categorising the tremor based on the key features of the examination, it is important to consider the most common tremor presentations to general practice. Below, we discuss clinical insights into common tremor syndromes, with less common tremor syndromes outlined in Table 4.
|
Table 2. Key aspects in taking a focused tremor history, with a short description of clinical relevance
|
|
Key aspect
|
Description of clinical relevance
|
|
Age at onset
|
- ET typically has a bimodal age distribution, peaking in the second and third decades of life and in the seventh and eighth decades of life28
- PD often manifests in older age groups, with its incidence rising after the age of 60 years4
|
|
Characteristics of onset and progression
|
- An abrupt onset could suggest an acute insult such as stroke; however, psychogenic tremors may also present acutely
- A gradually worsening tremor is often described in ET and PD
|
|
Triggering factors and relieving factors
|
- Tremor may be task specific in dystonic tremor
- ET is generally relieved by alcohol intake; however, this is a non-specific feature4
- Stress, anxiety and emotional excitement can worsen tremors in PD and various other forms of tremor29
|
|
Distribution
|
- The body parts affected by the tremor, as well as its symmetry, can be significant indicators of the underlying condition; for example, head tremor is common in ET and rare in PD, whereas a leg tremor is more common in PD than ET7
- ET commonly presents as a bilateral, mostly symmetric action tremor in the hands and arms
- In PD, tremor typically starts unilaterally7
|
|
Associated symptoms
|
- The patient should also be asked about other neurological symptoms that they may be experiencing
- PD is often associated with loss of dexterity, gait disturbance, hypophonia and stiffness. Noting other features, such as anosmia and REM sleep disturbance, may be supportive of a PD diagnosis14
|
|
Medication and substance history
|
- Antiseizure medications, antipsychotics, lithium, metoclopramide, antidepressants, alcohol withdrawal, steroids, β-adrenoceptor agonists, amiodarone, calcium channel blockers, chemotherapy agents, immunosuppressants such as tacrolimus, caffeine and nicotine can induce tremor
|
|
Family history
|
- In about half the cases of ET, the family history indicates an autosomal dominant inheritance pattern
- Although PD is generally sporadic, around 15% of patients do have a family history30
|
|
Impact on quality of life
|
- Assess the psychosocial impact and daily function
|
|
ET, essential tremor; PD, Parkinson’s disease; REM, rapid eye movement.
|
|
Table 3. Focused examination of tremor
|
|
Phase
|
Assessment technique
|
Illustration
|
Observations and clinical relevance
|
|
Initial observation
|
Start observing the patient’s tremor as they are called into the consultation room, paying attention to how they transition from sitting to standing and their gait
|
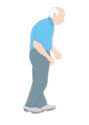 |
- Difficulty transitioning from sitting to standing may indicate parkinsonian syndromes, but may also indicate a proximal myopathy
- A stooped posture or shuffling gait with the presence of a tremulous upper limb that does not swing may also indicate parkinsonism
- A broad-based gait could suggest proprioceptive or cerebellar impairments
|
|
Assessment of resting tremor
|
Observe the patient in a resting position with their hands prone on their lap
|
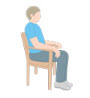 |
- Observe whether the patient has a resting tremor
- If a tremor is observed at rest, accentuation with mental tasks can be evaluated by asking the patient to close their eyes and name the months of the year backwards.4 Cognitive load will increase the amplitude or reveal a subtle intermittent rest tremor in PD31
|
|
Assessment of postural tremor
|
Ask the patient to position their arms outstretched and in the wing-beating position (arms horizontally oriented with the palms facing downward while the shoulders are in an abducted position and the elbows are flexed)
|
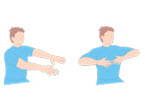 |
- This test reveals the severity of the proximal postural component of the tremor syndrome, which is often increased in ET4,7
- A wing-beating tremor with dystonic posturing is also a characteristic feature of Wilson’s disease4
|
|
Identifying the presence of dysmetria or intention tremor
|
Perform the finger–nose test: ask the patient to repeatedly touch their nose and then the examiner’s finger (this assesses coordination and may elicit tremors that worsen with targeted movement)
|
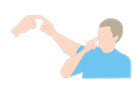 |
- An intention tremor is classically characterised by a crescendo increase in tremor as the finger reaches its target
- Intention tremors are classically associated with cerebellar pathology and are found in patients with cerebellar lesions from pathologies such as stroke or plaques from multiple sclerosis2
- Notably, intention tremors can also occur with ET, but in these cases they are typically not accompanied by other cerebellar signs, such as dysmetria
|
|
Task-specific tremor
|
Observe a task that results in tremor, such as drinking from a cup
Note how the tremor changes as the patient approaches the target
Pay attention to any compensatory strategies used (eg drinking with two hands instead of one)
|
 |
- Dystonic tremor is task or position specific with irregular ‘flurries’ of tremor observed
|
|
Bradykinesia
|
Ask the patient to perform thumb–index finger tapping for approximately 10 repetitions
Note changes in the speed and amplitude of the action over time
|
 |
- Bradykinesia is a cardinal feature of PD and refers to both the generalised slowness with decrementing amplitude of movement
|
|
Rigidity
|
Examine the tone of a relaxed limb by passively moving the joint throughout its range of motion
Note any cogwheel rigidity
|
 |
- Rigidity is a cardinal feature of PD, and typically manifests on the same side as a PD tremor4
- Cogwheel rigidity is thought to be due to a tremor superimposed on increased muscle tone. It manifests as a ratcheting pattern of resistance throughout the passive movement of a limb and can intensify with voluntary contralateral arm movements
|
|
Writing and drawing
|
Observe the patient while they write a long sentence
Ask the patient to draw an Archimedes spiral (see Figure 1)
|
|
- When writing a long sentence the following may be observed:
- Micrographic (progressively smaller handwriting) often indicates PD
- Uniform tremor oscillations may suggest essential tremor or primary writing tremor
- The Archimedes spiral task can reveal tremor characteristics and severity. When drawing an Archimedes spiral the following may be observed:32
- PD may show a tight, micrographic tremulous spiral
- ET often exhibits consistent oscillations, worse at the
- 2 o’clock – 8 o’clock axis
- Dystonic tremor may display irregular, multidirectional oscillations
|
|
ET, essential tremor; PD, Parkinson’s disease.
|
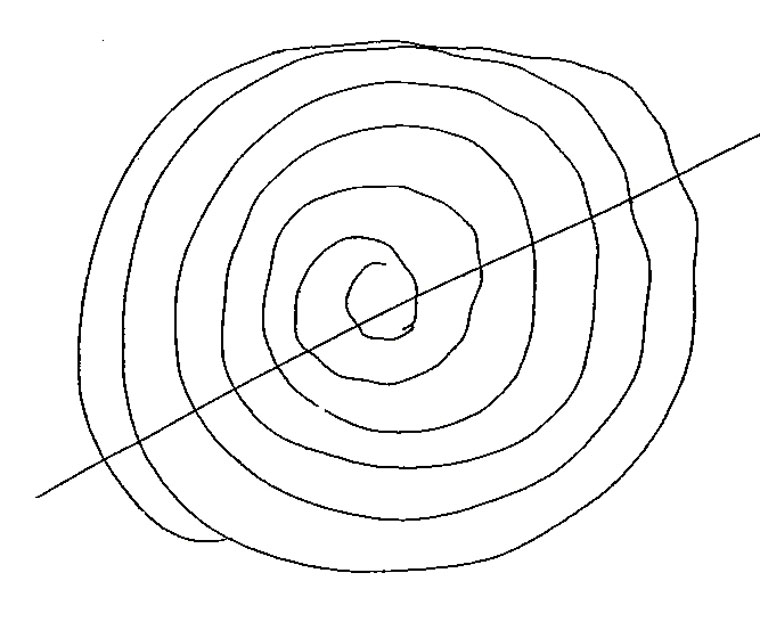
Figure 1. Archimedes spiral performed by a patient with a mild essential tremor syndrome. Note the tremor is in the typical 2 o’clock – 8 o’clock axis for essential tremor syndrome, with a line drawn by the clinician between these points.
|
Table 4. Less common tremor syndromes encountered in clinical practice
|
|
Tremor type
|
Clinical features
|
|
Cerebellar tremor
|
- Intention tremor with associated features of dysmetria, dysarthria and wide-based gait
|
|
Neuropathic tremor
|
- Action relatively symmetric limb tremor that may be associated with chronic inflammatory demyelinating neuropathy33
- Associated positive Romberg sign and neuropathy features
|
|
Orthostatic tremor
|
- High-frequency fine tremor typically in the legs that occurs shortly after standing, resulting in a tendency to fall if stationary3
|
|
Rubral tremor
|
- A low-frequency unilateral limb tremor worse with kinetic movement, often with a rest tremor component
- May develop acutely after a stroke (eg midbrain stroke)34
|
|
Multiple sclerosis-related tremor
|
- Intention and postural tremor are two major components in multiple sclerosis tremor
|
|
Tremors associated with genetic disorders
|
- Vary based on the underlying genetic condition; examples include Fragile X syndrome4 and Klinefelter syndrome4
|
|
Age-related tremor
|
- Late-onset non-disabling action tremor, particularly in patients with a high burden of cerebrovascular disease35
|
|
Indeterminate tremor
|
- Non-specific tremor features and failure to meet criteria for known tremor types or underlying neurological condition3
|
|
Isolated head tremor
|
- Tremor isolated to the head without clear dystonic features3
|
|
Palatal tremor
|
- Symptomatic palatal tremor involves low-frequency, semirhythmic movements of the soft palate, typically combined with ataxia, and is usually attributed to a lesion in the dentato-olivary pathway
|
Essential tremor syndrome
Essential tremor (ET) is the primary cause of action tremor worldwide, affecting approximately 1% of the population and increasing to 5% among those aged over 60 years.4 Despite its prevalence, ET remains frequently misdiagnosed.5 The disease imposes a significant burden, with an estimated one million US patients currently untreated.6 The pathophysiology of ET is thought to involve dysfunction in the cerebello-thalamo-cortical network, with degenerative changes in the Purkinje cells of the cerebellum.3
ET is characterised by an action tremor occurring without any other neurological condition.1 To fulfil the ET diagnostic criteria, a patient must have an isolated tremor syndrome characterised by bilateral upper limb action tremor lasting for at least three years, possibly involving tremor in other locations, including the head, voice or lower limbs.1 An ET tremor may be mildly asymmetric, initially affecting the upper limbs.4,7 The 2018 International Parkinson and Movement Disorder Society’s tremor classification allows for ‘soft neurological signs’ in ET, such as mild impaired tandem gait or subtle dystonic posturing, which may be referred to as ET plus syndrome.1
Management of ET starts with eliminating exacerbating medications and substances, such as caffeine. The evidence supports propranolol as an initial therapy, with later consideration of primidone.8,9 If first-line therapy fails, combination treatments or a transition to second-line agents like gabapentin or topiramate may be warranted.10,11 Existing treatments are often discontinued due to lack of effectiveness or tolerability, underscoring the urgent need for more effective therapeutic options.6 Interventional treatment includes incisionless magnetic resonance imaging–guided focused ultrasound (MRIgFUS), which targets nuclei in the thalamus, and the invasive insertion of a deep brain stimulation device.3
Parkinsonism and tremor
Tremor is most commonly associated with idiopathic Parkinson’s disease (PD) with 40–65% of PD patients having a resting tremor at presentation.3 PD affects approximately 1% of adults aged over 70 years,4 and results from the degeneration of dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra, causing striatal dopamine deficiency and disrupted motor control.3
A parkinsonian tremor is a resting tremor of 4–7 Hz frequency,3 often starting unilaterally in one distal upper limb (‘pill-rolling’).An action (kinetic) tremor develops in a significant proportion of PD patients as the disease progresses.12 The kinetic tremor in PD characteristically has a re-emergence postural tremor, which is a brief delay in tremor emergence after holding a certain posture.13 Accompanying features required for a PD diagnosis include decrementing bradykinesia, cogwheel rigidity and postural instability. Noting other abnormalities, including gait disturbance with the presence of a tremulous distal upper limb that does not swing, is useful. Response to levodopa is a component of the diagnostic criteria and is first-line treatment.14
In other parkinsonian syndromes, like Lewy body dementia, progressive supranuclear palsy, multiple system atrophy and vascular parkinsonism, a rest tremor is less prevalent.15 However, other forms of kinetic tremor may be present, such as the irregular, jerky postural and kinetic tremor seen in multiple system atrophy parkinsonian subtype.16
Dystonic tremor
Dystonia is a movement disorder causing sustained muscle contractions that result in abnormal, repetitive and often twisting movements. Dystonic tremor may worsen with specific voluntary actions, and includes unintentional muscle activation in adjacent areas to the tremor.17 Dystonic tremor is a specific form of tremor that occurs when sustained contractions of dystonic muscles have an overlying spasm that appears rhythmic. The tremor is usually an action tremor that has a postural component.4
The most common areas affected by dystonic tremor are the neck and upper limbs.3 When observing dystonic tremor, a distinctive feature is an irregular, jerky multidirectional tremor with ‘flurries’ that deviate from a consistent oscillatory pattern.3 On examination, there may be specific clues present, such as:
- geste antagoniste (when a specific manoeuvre temporarily eases the tremor); for instance, touching the cheek might diminish a neck tremor in cervical dystonia17,18
- null point (a particular joint position where the dystonic tremor is either greatly reduced or absent); this may be noted when rotating the head in a certain direction in cervical dystonia.17,18
Botulinum toxin injections are considered first-line treatment for many forms of focal dystonia, including cervical dystonia.3 Other medications, such as anticholinergic agents like trihexyphenidyl, may be considered. Treatment-refractory patients may be appropriate for MRIgFUS or deep brain stimulation procedures.
Medication-induced tremor
Medication-induced tremor arises from various drugs, often by enhancing physiological tremor. Common culprits include steroids, caffeine and β-adrenoceptor agonists like salbutamol. Tremors can also result from medication toxicity, such as antiseizure medications. Sodium valproate causes tremors resembling ET in up to 25% of users. The severity of the tremor may be dose dependent (and may occur within the therapeutic dose range of the drug).19,20
Drug-induced tremor secondary to lithium is the most common tremor encountered in clinical practice. Up to 65% of individuals on lithium experience tremor.20 This tremor is typically postural and kinetic, with a high frequency (eg 8–12 Hz). This can manifest across a broad range of lithium concentrations and a normal lithium concentration does not rule out drug-induced tremor, especially in the elderly and those with chronic kidney disease. Antidepressants such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors and tricyclic antidepressants can cause an enhanced physiological tremor, or worsen an underlying tremor syndrome.20
Antipsychotic-induced extrapyramidal side effects can present as tardive tremor or drug-induced parkinsonism, often with bilateral upper limb resting and kinetic tremor. There may be other drug-induced features, such as tardive dyskinesia (eg involuntary oral buccal movements).3 Other dopamine-depleting drugs, such as metoclopramide, can have a similar presentation.20
Other important causes of drug-induced tremor are immunosuppressive medications, such as tacrolimus.20 They cause an action postural or intention tremor that is related to dose. Other causes of tremor include amiodarone, calcium channel blockers and chemotherapy agents (including vincristine, cisplatin, paclitaxel, doxorubicin, cytarabine and methotrexate).20
Enhanced physiological tremor
Enhanced physiological tremor is a high-frequency symmetric postural and kinetic tremor in the upper limbs that may intensify under specific environmental or physiological conditions. If not caused by medications, other considerations include anxiety, fatigue, illicit drug use, alcohol withdrawal, hypoglycaemia, excessive caffeine consumption, hyperthyroidism and toxin exposure.3
Functional tremor syndrome
Functional tremor syndrome can present in isolation or with other functional neurological disorder symptoms. Patients with functional tremor may report a sudden onset following a physical event like injury or illness, or a stressful life event.21 Features suggesting a functional tremor syndrome include fluctuating findings of the tremor location, frequency and activation characteristics.21 There may be accompanying history of somatisation symptoms or psychiatric history.21 If functional tremor is suspected, additional specific provocative features to note include the following:
- Distractibility is assessed with distraction tasks. Functional tremors may improve, subside or change in frequency and amplitude during distraction tasks. For example, the examiner should monitor for interruption of contralateral limb tremor while asking the patient to perform finger tapping.21
- Entrainability is assessed by observing whether the frequency of the symptomatic limb postural or rest tremor can be synchronised with a voluntary rhythmic movement in the contralateral side (eg to the beat of an examiner’s clap).21
- Suggestibility can be noted during the neurological examination. For example, note migration of the tremor location to a previous asymptomatic area while assessing the tone of a limb.21
Masquerades of tremor and red flags
Tremors are commonly encountered in general practice, and recognising their masquerades is essential for general practitioners (GPs) to identify patients needing urgent management, including the treatment of systemic conditions. Enhanced physiological tremor prompts a thorough assessment for other systemic causes, as discussed earlier. In addition, consideration of other forms of hyperkinetic movements that may resemble a tremor is required.
Myoclonus can appear similar to tremor, but it differs from tremor in its lack of rhythm and presence of directionality, whereas tremor oscillates between the same points. Myoclonus may also be drug induced or relate to systemic disease (eg due to renal or liver failure, CO2 retention or medication side effects). Patients with negative myoclonus (also known as asterixis) from CO2 retention or liver failure may describe their own condition as a ‘tremor’.4
Although rare, certain red flags in tremor evaluation demand urgent attention.22 An abrupt onset with accompanying symptoms like weakness, loss of dexterity or slurred speech raises concerns for stroke. A rapid progression of tremor (days–weeks) with dysarthria, ataxia, seizures or gait disturbances raises concern for a possible immune-mediated disorder, underlying neoplasm or drug toxicity.22 Patients with a sudden-onset unilateral inability to use a limb with continuous focal ‘twitching’ that can spread to the face may have continuous focal seizures due to epilepsia partialis continua. Encountering these signs should prompt clinicians to consider referral to the emergency department for further assessment.
Investigations to consider
If an acquired cause or treatable metabolic disorder is suspected, routine blood tests can be useful. These may include a full blood count, urea, electrolytes, creatinine, liver function tests, blood glucose, thyroid function and relevant drug levels.
Generally, magnetic resonance imaging of the brain is recommended for patients with tremor if there is suspicion of structural brain abnormalities, an asymmetric tremor with sudden onset that may indicate vascular pathology or when a heritable neurodegenerative or metabolic disorder is considered in the differential diagnosis.23
Conclusion
Tremor has a diverse range of aetiologies and requires a framework for assessment. GPs are pivotal in the diagnostic process and management of tremor syndromes, including identifying common treatable conditions and masquerades.
Key points
- Tremors present a complex diagnostic challenge for many clinicians due to the broad range of causes.
- A framework for characterising tremor is essential for accurate diagnosis.
- Undertake a thorough drug history to identify possible medication-induced tremor.
- Consider red flags in a tremor syndrome to identify other systemic medical conditions.