Medicine use is one of the most common interventions in healthcare. A general practitioner (GP) in Australia typically prescribes 85.5 medicines per every 100 consultations.1 Part of good prescribing practice is selecting the most appropriate medicine and dosage to meet an individual’s therapeutic needs for a suitable duration.2 Prescribing is a dynamic process that requires continuing reassessment and monitoring. The risk–benefit profile of medication is constantly shifting, especially in older people with multimorbidity. Deprescribing encompasses the concept of good prescribing practice and refers to the withdrawal of medicine that is no longer warranted.3,4
Why is inappropriate polypharmacy an issue for older people?
In 2020–21, over half (54%) the medicines dispensed under the Pharmaceutical Benefits Scheme and the Repatriation Schedule of Pharmaceutical Benefits were for people aged 65 years and above.5 In addition to old age and comorbidities, the individual prescriber is a major risk factor for polypharmacy, defined as the concurrent use of five or more medicines.6 Polypharmacy is considered inappropriate when the potential harm of taking multiple medicines outweighs the potential benefits. Inappropriate polypharmacy in older people has a negative impact on cognition, health-related quality of life and mortality.7–9 Although some medicines may be therapeutically indicated for an individual, polypharmacy paves the way for an increased risk of drug–drug interactions, medicine errors due to complex regimens and increased healthcare expenditure.10,11 Because of frailty, older people are most vulnerable to the negative consequences of polypharmacy.12 Polypharmacy increases the treatment burden for a patient and, paradoxically, may lead to the underprescribing of indicated medicines.7 Complex medication regimens are also associated with non-adherence, contributing to poor patient outcomes, and medicine wastage.13
High-risk prescribing for older patients
The use of potentially inappropriate medicines (PIMs) is common in polypharmacy, but also occurs in the absence of polypharmacy.14 PIMs are medicines with an unfavourable benefit–harm ratio or no clear evidence-based indication that are not cost-effective or are used instead of a safer and more effective alternative.15,16 For example, anticholinergic and sedative medicines are often considered PIMs in older people because they are associated with serious adverse outcomes in this group, including increased frailty, reduced appetite and impaired cognitive and physical function.17,18
Prescribing cascades occur when a drug-related adverse reaction is misinterpreted as a new medical condition and a second medicine is used to manage the symptoms.19 An example of this is the use of loop diuretics to manage ankle oedema arising from the use of calcium channel blockers.20 Prescribing cascades are preventable. GPs should always first consider a patient’s current medicines as the cause of any new or ongoing troublesome symptoms. The question to ask is, ‘Are any of these medicines contributing to the symptoms experienced by my patient?’
Why should GPs consider deprescribing?
Deprescribing is an intervention to reduce inappropriate polypharmacy and high-risk prescribing (including PIMs and prescribing cascades; Figure 1). The common goals of deprescribing in older people are to reduce pill burden, improve health outcomes and reduce the risk of specific geriatric syndromes, such as falls and cognitive impairment;23,24 the ultimate goal is to improve quality of life.
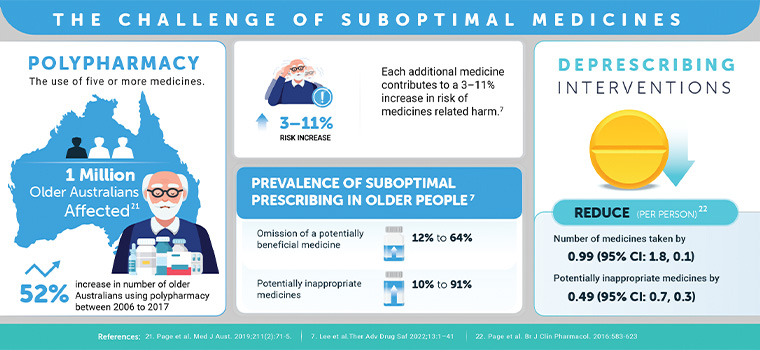
Figure 1. Snapshot of polypharmacy, suboptimal use of medicines and deprescribing interventions.
The decision to deprescribe encompasses the concept of patient-centred care by focusing on an individual’s treatment goals and preferences, all of which evolve as a person ages and their functional status changes. The process of deprescribing is important because it provides a prime opportunity to reassess an individual’s health status and reconcile their current medicines list.
What tools are available to help with deprescribing?
GPs are very familiar with the concept of discontinuing ineffective medicines or those causing adverse effects worse than the condition being treated. However, with multiple competing priorities, many prescribers will not feel as confident with a shared decision-making process that involves a comprehensive assessment and medicines reconciliation with a focus on identifying suitable targets for cessation. Hence, several tools have been developed to facilitate decision making in this type of deprescribing (Table 1). For example, the CEASE (Current medicines, Elevated risk, Assess, Sort, Eliminate) algorithm (Figure 2) and ERASE (Evaluate, Resolved conditions, Ageing normally, Select targets, Eliminate) approach (Figure 3) are clinical mnemonics developed to aid deprescribing. Table 2 lists the resources available for the specific medicines prescribers may consider targeting first.
| Table 1. Tools to aid deprescribing |
| Tool |
Purpose |
Example of applicability |
Reference |
Open access? |
| MATCH-D criteria (Medication Appropriateness Tool for Comorbid Health conditions during Dementia) |
To optimise medicine use in people with dementia |
For people with early stage dementia, consider stopping antiplatelet, anticoagulant and antithrombotic agents used for preventative measures |
Page et al25 |
Yes, with the tool freely available at http://www.match-d.com.au/ |
| Validated prescribing appropriateness criteria for older Australians |
Australian prescribing indicators to help identify common medicine-related problems in older people |
Patient taking a PPI is NOT taking a medication that may cause dyspepsia unless prescribed for gastroprotection |
Basger et al26 |
Yes |
| Beers Criteria® |
Explicit list of potentially inappropriate medicines in older people |
Avoid using antipsychotics for behavioural problems of dementia |
American Geriatrics Society Beers Criteria® Update Expert Panel27 |
No |
| STOPP (Screening Tool for Older Peoples Prescriptions) |
Explicit rules for ceasing certain medicines |
Cease calcium channel blockers with chronic constipation |
O’Mahony et al28 |
Yes |
| Deprescribing algorithm modified from the Good Palliative – Geriatric Practice (GPGP) algorithm |
Decision tree diagram for deprescribing |
- Inappropriate prescription
- Adverse effects or interaction
- Drug taken for symptom relief
- Drug intended to prevent serious future events
|
Page et al29 |
No |
| CEASE algorithm (Figure 2) |
Guide the deprescribing process during a doctor–patient encounter |
Current medicines, Elevated risk, Assess, Sort, Eliminate |
Scott and Le Couteur30 |
Tool provided in this article |
| ERASE approach (Figure 3) |
Review diagnoses and associated medicines
|
Evaluate diagnoses through the consideration of Resolved conditions, Ageing normally, Selecting appropriate targets to Eliminate unnecessary diagnoses and medicines |
Page and Etherton-Beer6 |
Tool provided in this article |
| Prescribing and deprescribing in CKD |
Optimising medicine use in people with CKD |
List of commonly prescribed medications that may require dose reduction or cessation in people with CKD (eg diabetes medications) |
Manski-Nankervis et al31
|
Yes |
| CCB, calcium channel blocker; CKD, chronic kidney disease; PPI, proton pump inhibitor. |
| Table 2. Deprescribing guidelines for specific medicines/drug classes |
|
| Medicine/drug class |
Risk for use in older people |
Relevant deprescribing guidelines |
| Allopurinol |
Worsening renal dysfunction and serious skin toxicity |
A |
| Anticholinergics |
Cognitive impairment and urinary retention |
B |
| Antihyperglycaemics |
Hypoglycaemia and related morbidity |
A, C |
| Antihypertensive agents |
Falls |
A |
| Antipsychotics |
Parkinsonism or extrapyramidal symptoms, falls |
A, B, C |
| Aspirin |
GI bleeding |
A |
| Benzodiazepines and/or Z-drugs |
Sedation, falls, confusion, dependence |
A, C |
| Bisphosphonates |
Hypocalcaemia |
A |
| Cholinesterase inhibitors and memantine |
GI upset, urinary incontinence, bradycardia |
A, C |
| Gabapentinoids |
Sedation, ataxia, falls |
D |
| Glaucoma eye drops |
Mostly well tolerated but may no longer be indicated if life expectancy is limited |
A |
| NSAIDs |
GI bleeding, renal failure, exacerbation of cardiovascular diseases |
A |
| Opioids |
Sedation, falls, fractures, dependence |
A, B, E |
| Proton pump inhibitors |
Long-term use increases the risk of fractures, altered absorption of nutrients and some medicines |
A, B, C, Turner et al32 |
| Sedating antihistamines |
Falls, fractures, confusion, drowsiness |
B |
| SSRIs and SNRIs |
Falls |
B |
| Statins |
Myopathy, rhabdomyolysis and fatigue |
A |
| Tricyclic antidepressants |
Falls, sedation, anticholinergic adverse effects |
B |
| Vitamin D and calcium |
Falls, hypercalcaemia |
A |
A, Primary Health Tasmania (https://www.primaryhealthtas.com.au/resources/deprescribing-resources/);
B, New South Wales Therapeutic Advisory Group (http://www.nswtag.org.au/deprescribing-tools/);
C, Bruyère Research Institute (https://deprescribing.org/resources/deprescribing-guidelines-algorithms/);
D, Canadian Medication Appropriateness and Deprescribing Network (https://www.deprescribingnetwork.ca/patient-handouts);
E, Victorian Department of Health (https://www.health.vic.gov.au/sites/default/files/migrated/files/collections/policies-and-guidelines/safe-opiod-use/recommendations-for-deprescribing-or-tapering-opioids---for-health-professionals.pdf).
GI, gastrointestinal; NSAIDs, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs; SNRIs, serotonin noradrenaline reuptake inhibitors; SSRIs, selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors; Z-drugs, zopiclone, eszopiclone, zaleplon and zolpidem. |

Figure 2. The CEASE (Current medicines, Elevated risk, Assess, Sort, Eliminate) algorithm.

Figure 3. The ERASE (Evaluate, Resolved conditions, Ageing normally, Select targets, Eliminate) approach for undiagnosing in older people.
Approaches to successful and safe deprescribing
Deprescribing interventions appear to cause few adverse outcomes (Table 3).22,33–35 Physicians should consider tapering medicines more likely to cause withdrawal symptoms and those that cause rebound syndromes if ceased abruptly. Such medicines include central nervous system-active medicines, proton pump inhibitors, beta-blockers and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.36 In most cases, adverse drug withdrawal events are not severe and, if necessary, the withdrawn medicine (or an alternative) can be restarted. When there is more than one medicine to deprescribe, GPs should first prioritise the medicine with the highest risk of harm and the lowest anticipated benefit from continued use. The prioritisation matrix (Figure 4) is unique to each individual, and GPs are familiar with using risk stratification strategies in their day-to-day practice.
| Table 3. Potential pitfalls of a deprescribing intervention |
| Potential consequences |
Examples |
Suggestions |
| Return of original disease symptoms |
Symptoms of reflux on discontinuation of a proton pump inhibitor
Rebound insomnia on discontinuation of temazepam |
‘Stop slow, go low’ approach:
- short-term pharmacological substitution or management
- taper the medicine
- psychological support (if applicable)
- periodic monitoring of the original disease
|
| Adverse drug withdrawal events |
Sleep disturbance, tremor, irritability, anxiety, and palpitation on discontinuation of a benzodiazepine |
‘Stop slow, go low’ approach:
- stop one medicine at a time (refer to Figure 4)
- taper the medicine
- close monitoring
|
| Unmasking drug interactions |
For patients on warfarin, altered INR on discontinuation of amiodarone |
Thorough medication review before deprescribing to identify any potential pharmacokinetic interactions |
| Damaging patient–doctor relationship |
Patients may interpret deprescribing as ‘giving up’ |
Shared decision making and patient collaboration:
- engage patients (and their caregivers) in every step of the intervention
- clear explanation of expected risks and benefits
- provide written patient information
- psychological support where needed
|
| Deprescribing-related complications |
An occurrence of myocardial infarction being attributed to discontinuing a statin |
- Careful consideration of the benefit–harm ratio of a preventative medicine is key, taking into account an individual’s life expectancy
- Consider other options for risk management (eg lifestyle changes)
- Document all reasonable grounds for stopping a medicine
|
| INR, international normalised ratio. |
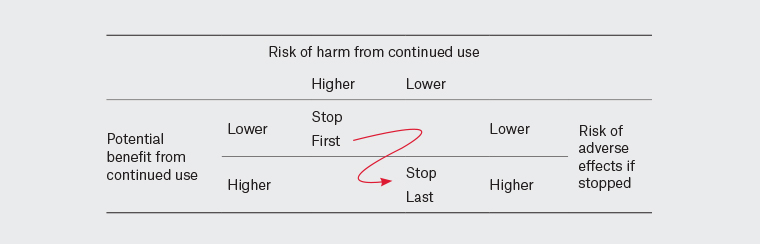
Figure 4. Prioritisation matrix for deprescribing.
Outcomes of deprescribing
A 2016 systematic review of deprescribing polypharmacy found that the intervention did not alter mortality in randomised controlled trials (odds ratio [OR] 0.82; 95% confidence interval [CI]: 0.61, 1.11), but did reduce mortality in non-randomised studies (OR 0.32; 95% CI: 0.17, 0.60).22 Although the benefits of deprescribing on health outcomes are uncertain, recent evidence suggests it is safe and feasible,22,37–39 with the caution that many deprescribing studies are of low quality with small participant numbers and short follow-up periods.40
What do patients think of deprescribing?
Recent studies of patient attitudes towards deprescribing found that 84–90% were willing to withdraw one or more of their medicines when suggested by the prescriber.41,42 Although individual cases vary, most people accept their GP’s opinion and advice. One of the critical attributes of deprescribing is ‘patient-centred care’.43 Partnering with the patient is an important part of patient-centred care, which encompasses the concept of individualised care by assessing a person’s needs that define the overall goals of care in the patient context.44
Barriers and enablers to deprescribing intervention
Many factors impede implementation of deprescribing as part of routine clinical care,40 including:
- clinician-related barriers: lack of time or resources, competing priorities, inadequate communication between different healthcare professionals about medical history or the medicine withdrawal plan, possible lack of knowledge and skills
- patient-related barriers: inadequate knowledge about deprescribing or medication review, perceived or potential reliance on certain medicines, personal beliefs and attitudes
- system-related barriers: gaps in transitional care between different healthcare settings, insufficient health campaign on deprescribing, poor design of GP prescribing software that warns of significant drug interactions, limited availability of effective non-pharmacological treatment options.
Interprofessional collaboration between GPs, pharmacists and nurses can address some of these barriers, in particular GPs’ lack of time and resources to perform a detailed medication review (Box 1).
45 Pharmacist-led medication reviews identify medicines suitable for deprescribing, and nurses can undertake the monitoring and patient support components.
46,47 Patients favour the involvement of pharmacists in the process,
48 and pharmacists can address important patient-related barriers, such as inadequate knowledge about medicine cessation. Collaborative deprescribing also empowers patients to be more proactive and involved in their own care.
| Box 1. Case study |
|
Tom (age 80 years) sees you today for a repeat prescription on all of his usual medicines for his chronic conditions. Tom’s medical conditions include hypercholesterolaemia, hypertension, gout, chronic constipation, and insomnia, for which he takes a daily dose of rosuvastatin 10 mg, ramipril 5 mg, hydrochlorothiazide 25 mg, allopurinol 150 mg, amitriptyline 10 mg and docusate sodium/senna 50 mg/8 mg. During the consultation, you ask Tom how he feels about all the medicines he is currently taking, with a focus on his medication adherence, possible side effects, his personal views towards each medicine and cost. Tom expresses his concern to you over side effects and increased treatment burden. You then ask Tom if he would prefer stopping or reducing some of his medicines. Tom agrees to give it a try, and asks for your recommendations. You decide to use the CEASE algorithm to help with your decision making:
- You reconcile Tom’s current medicines (or provide a referral to an accredited pharmacist for a Home Medicines Review).
- You are aware of the different tools available to help you identify medicines that may be more harmful to Tom. By referring to the Beers and STOPP criteria, you identify:
- amitriptyline, which is highly anticholinergic and sedating, may cause orthostatic hypotension, worsen constipation and could be a prescribing cascade with docusate sodium/senna
- hydrochlorothiazide, because it may exacerbate gout and could be a prescribing cascade with allopurinol.
- You assess the benefit–harm trade-offs of these medicines in the context of Tom’s age, concurrent medicines, overall physical health, possible pill burden, personal preferences, treatment goals, and social and financial support. Based on this, you further identify the following as potential deprescribing targets:
- rosuvastatin for primary prevention
- ramipril, considering the blood pressure targets for Tom’s age
- docusate sodium/senna, due to the evidence of inefficacy
- allopurinol, which may be ceased if Tom has been asymptomatic for the past 12 months and diuretic has been ceased or if Tom’s dietary and alcohol intake have improved.
- By using the prioritisation matrix and taking into account Tom’s preferences, you decide to prioritise ceasing amitriptyline over the other medicines because it has a comparatively higher risk of harm from continued use.
- You propose a medication withdrawal plan using the relevant drug-specific deprescribing guideline to gradually taper the dose of amitriptyline. Finally, you inform Tom of what to expect and reassure him that you will monitor his progress closely for improvement in outcomes or the onset of adverse events. You also provide Tom with a leaflet on managing insomnia through lifestyle modifications.
On future visits, if Tom is responding well and no longer has constipation, you could then suggest the next plan is to deprescribe his other medicines. |
Conclusion
Deprescribing should be a core component of the clinical care provided to older people by GPs because this intervention is a key antidote to the harms caused by inappropriate polypharmacy. GPs can make deprescribing a routine part of their day-to-day clinical practice by using evidence-based practical deprescribing tools and engaging in collaborations with pharmacist and nurse colleagues.
Key points
- Deprescribing is an intervention to reduce polypharmacy and high-risk prescribing.
- The ultimate goal of deprescribing is to improve patient outcomes.
- GPs can deprescribe medicines safely by ensuring slow dose tapering and patient engagement.
- Deprescribing is acceptable to patients.
- Deprescribing requires an individualised approach and can be supported by a multidisciplinary team.